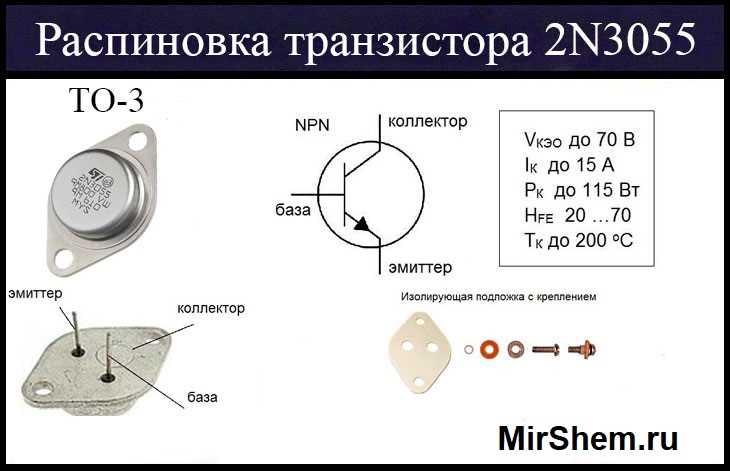
Are you an electronics enthusiast or a professional electrical engineer seeking a high-performance NPN transistor for your next project? Look no further as we delve into the intricate details and superior capabilities of the highly sought-after 2n3055g transistor.
This comprehensive guide not only explores the technical specifications of the 2n3055g, but also highlights its versatile applications across various industries. From power amplifiers to voltage regulators, this transistor has revolutionized the field of electronics with its remarkable features and exceptional performance.
In this article, we embark on an enlightening journey as we decipher the significant details encrypted within the 2n3055g datasheet. Through a meticulous analysis of its key parameters, we shed light on its reliability, power dissipation, and current gain characteristics, providing you with a deeper insight into its functionalities.
Prepare to be captivated by the powerful capabilities of the 2n3055g transistor as we unravel its secrets and elucidate how it can elevate the performance of your next electrical project to unprecedented heights.
Overview of 2n3055g Datasheet

In this section, we will provide a comprehensive overview of the datasheet for the 2n3055g component. The 2n3055g datasheet contains valuable technical information and specifications that are essential for understanding the functionality and capabilities of this electronic component. Through this overview, we aim to provide a clear and concise summary of the key details presented in the datasheet.
The overview will cover various aspects, including the electrical characteristics, pin configuration, and recommended operating conditions of the 2n3055g component. Additionally, it will outline the typical applications and advantages of using the 2n3055g in electronic circuit designs. The aim is to present a comprehensive understanding of the datasheet to assist engineers, hobbyists, and enthusiasts in effectively utilizing the 2n3055g component in their projects.
Additionally, the overview will highlight any important considerations or limitations that one should be aware of when working with the 2n3055g component. This will provide users with a well-rounded understanding of the component’s performance and potential challenges that may arise during implementation.
| Key Topics Covered in 2n3055g Datasheet Overview: |
| 1. Electrical characteristics and specifications |
| 2. Pin configuration and functionality |
| 3. Recommended operating conditions |
| 4. Typical applications |
| 5. Advantages and benefits of using 2n3055g |
| 6. Considerations and limitations |
By providing a comprehensive overview of the 2n3055g datasheet, we aim to equip readers with the necessary knowledge and understanding to harness the full potential of this electronic component in their designs. This overview serves as a starting point for further exploration and in-depth analysis of the datasheet for detailed technical specifications and application-specific information.
Key Specifications and Electrical Characteristics
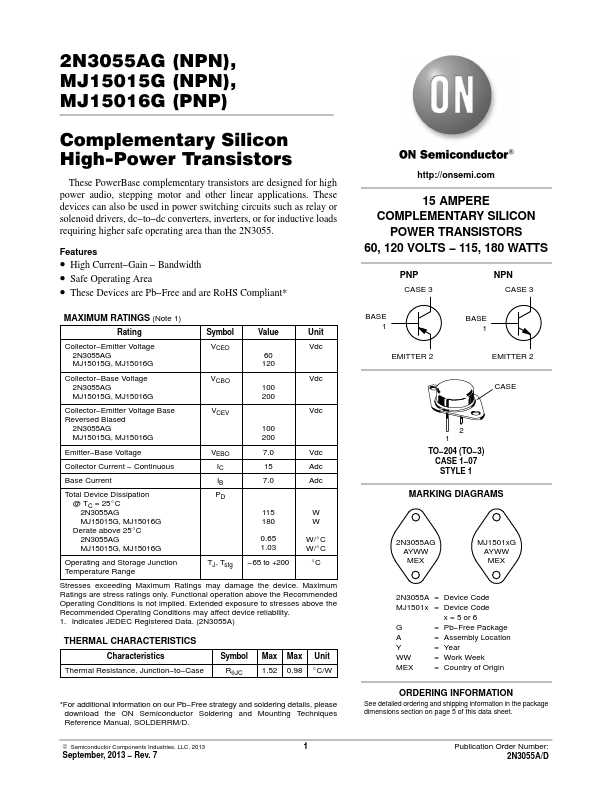
In this section, we will explore the key specifications and electrical characteristics of the component under discussion. These specifications provide essential information about the operating conditions and performance of the device, enabling users to make informed decisions and effectively utilize it in their applications.
1. Power Handling Capacity
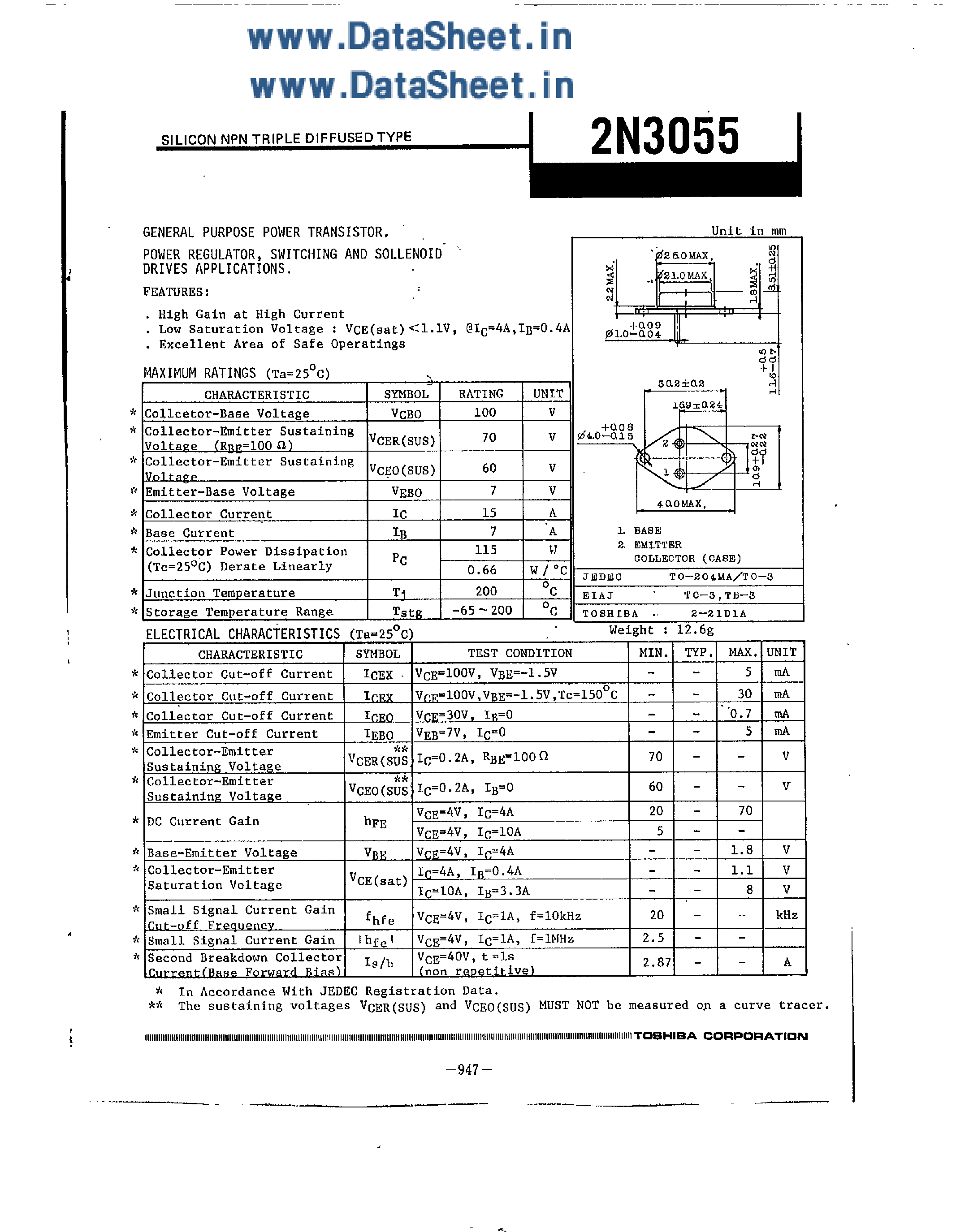
The power handling capacity of the component refers to its ability to handle and dissipate electrical power without being damaged. It is an important characteristic to consider when designing circuits or systems that require high power levels. The higher the power handling capacity, the more robust the component is in demanding applications.
2. Current Rating
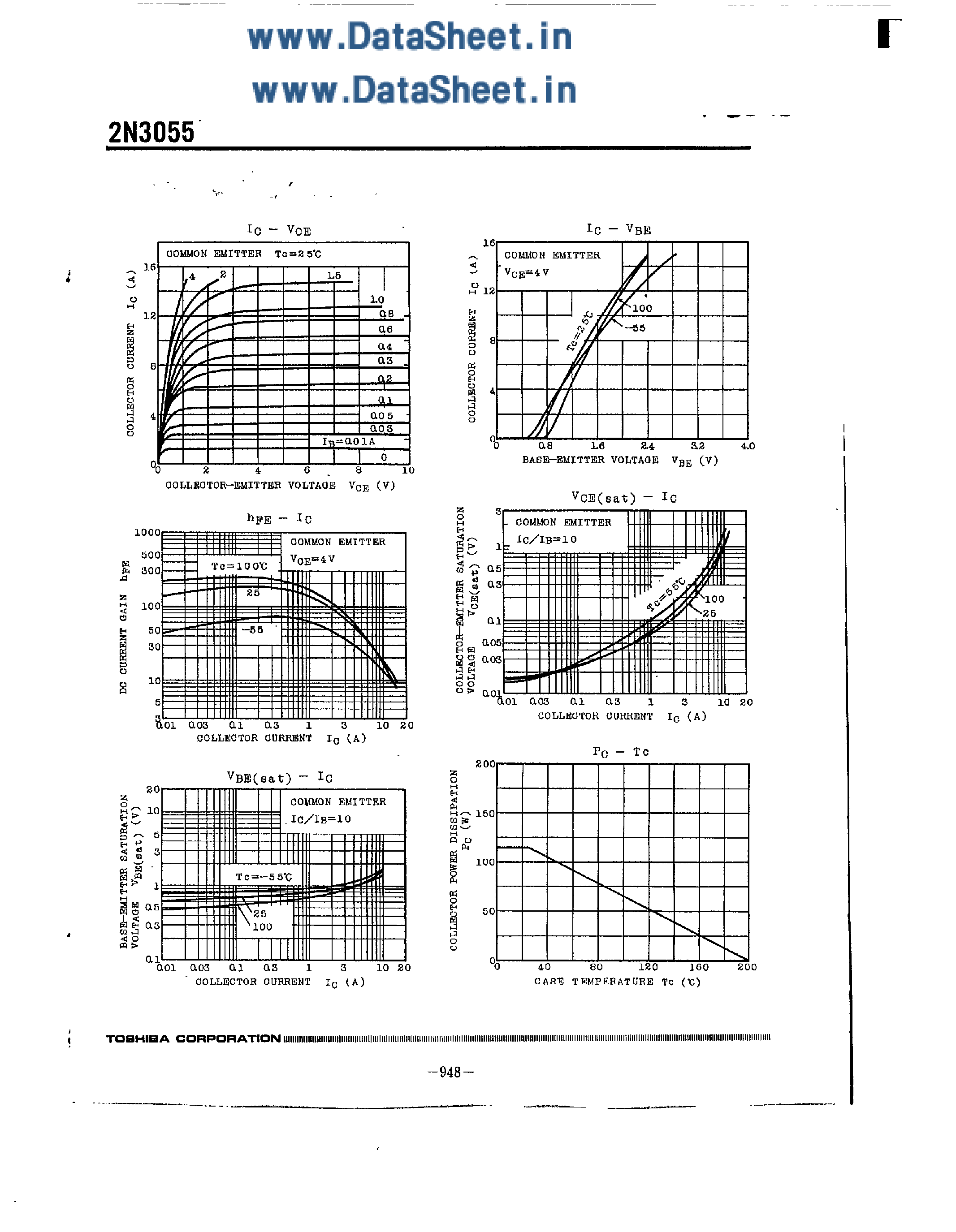
The current rating of the component indicates the maximum amount of electric current it can safely carry. It is crucial to ensure that the component’s current rating is suitable for the intended application to prevent overheating and potential damage. By understanding the current rating, users can determine the component’s compatibility with their specific circuit requirements.
3. Voltage Rating
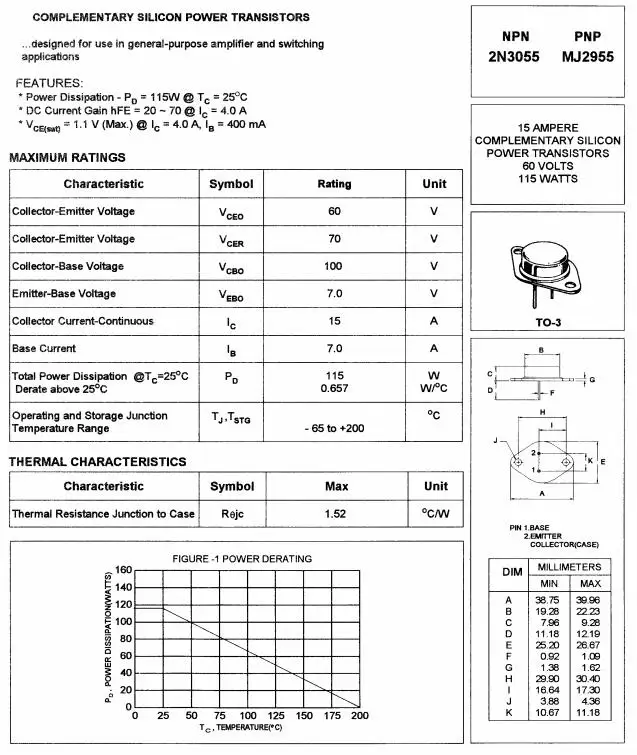
The voltage rating of the component specifies the maximum voltage it can withstand without breakdown or failure. It is essential to select a component with a voltage rating that exceeds the expected voltage levels in the circuit to ensure reliable performance. Understanding the voltage rating is crucial for avoiding electrical breakdowns and ensuring the longevity of the component.
4. Gain and Beta
The gain, also known as beta, is a critical parameter for transistors like the 2n3055g. It represents the ratio of the output current to the input current and determines the amplification capabilities of the device. A higher gain value indicates better amplification performance. Understanding the gain characteristics of the component helps in selecting the appropriate component for specific signal amplification requirements.
5. Frequency Response

The frequency response of the component defines its ability to handle signals of different frequencies. It determines the range of frequencies that the component can accurately amplify or pass through. By examining the frequency response characteristics, users can ensure compatibility with their application’s frequency range and achieve optimal performance.
These key specifications and electrical characteristics provide a comprehensive understanding of the capabilities and limitations of the component, enabling users to make informed decisions and design circuits that meet their specific requirements. It is essential to consult the component’s datasheet for detailed information on these specifications before selecting and implementing it in any electronic design project.
Applications and Circuit Design Considerations
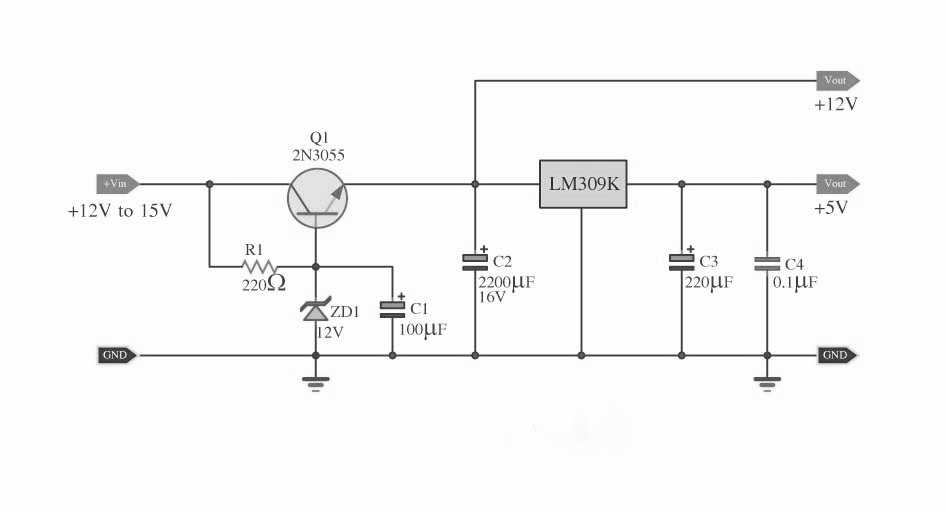
In this section, we will explore various applications and circuit design considerations for a power transistor. Understanding the potential uses and design principles can help maximize the performance and efficiency of the device.
- Power Amplification: The transistor can be used in audio and RF power amplifiers to enhance the signal strength while maintaining low distortion.
- Power Supply Regulation: The transistor can be incorporated into linear power supply circuits to regulate the output voltage and provide a stable power source.
- Motor Control: The transistor can drive motors with high current requirements, making it suitable for applications such as robotics and industrial machinery.
- Electronic Ballasts: The device can operate at high frequencies and handle large currents, making it ideal for electronic ballasts in fluorescent and HID lighting systems.
- Switching Applications: The transistor can be used as a switch in various circuits, such as DC-DC converters, switching regulators, and motor control switches.
When designing circuits with the transistor, it is important to consider certain factors to ensure optimal performance. These considerations include:
- Heat Dissipation: The transistor can generate significant heat during operation. Proper heat sinking and thermal management techniques should be implemented to prevent overheating and ensure long-term reliability.
- Maximum Ratings: Understanding the device’s maximum ratings, such as voltage, current, and power dissipation, is crucial to avoid damaging the transistor and ensure safe operation.
- Biasing and Drive Requirements: The transistor requires adequate biasing and drive voltage to operate in its active region. Proper biasing and drive circuitry should be designed to achieve the desired performance.
- Protection Circuitry: Incorporating protection circuitry, such as over-current and over-voltage protection, can safeguard the transistor and the overall circuit from potential failures and damage.
- Feedback and Stability: Proper feedback and compensation techniques should be employed to ensure stability and prevent oscillations in amplifier and regulator circuits.
By considering these applications and circuit design considerations, engineers can effectively utilize the potential of the transistor and create robust and efficient electronic systems.