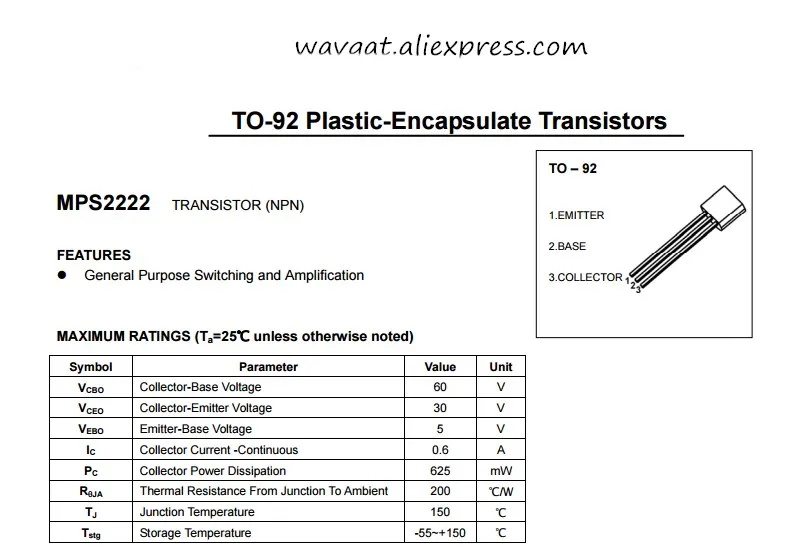
Welcome to this comprehensive guide that aims to explore the incredible potential and capabilities of two widely used transistors – the 2N2222A and 331. These transistors have proven to be extremely versatile and reliable components in a wide range of electronic applications. In this article, we will delve into the intricate details of their specifications, discussing their electrical characteristics, power ratings, and much more.
The 2N2222A and 331 transistors are among the most popular choices among electronic engineers and hobbyists due to their exceptional performance and reliability. These small, yet powerful devices are often utilized in various amplification and switching circuits, making them essential components in audio amplifiers, signal processors, and digital logic circuits. Understanding their specifications is crucial for achieving optimal results and maximizing the efficiency of your electronic projects.
When it comes to electrical characteristics, the 2N2222A and 331 transistors exhibit remarkable similarities. Both transistors offer a high collector current rating, ensuring ample current flow through the device. This characteristic makes them ideal for applications that require high power output or efficient signal amplification. Furthermore, these transistors boast a low power dissipation, ensuring minimal heat generation even during extended operation, which is essential for maintaining the overall stability and reliability of the circuit.
In addition to their outstanding electrical characteristics, the 2N2222A and 331 transistors also possess excellent gain properties. Both transistors feature a high current gain, ensuring effective amplification of weak input signals. This characteristic allows for accurate and efficient signal processing, enabling the creation of audio systems with improved audio fidelity and clarity. Moreover, these transistors exhibit low noise levels, contributing to the overall quality of the amplified signal.
Throughout this guide, we will explore the various specifications of the 2N2222A and 331 transistors in detail, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of their performance capabilities. By familiarizing yourself with these specifications, you will be equipped with the knowledge necessary to select the appropriate transistor for your specific application and achieve optimal results in your electronic projects.
Key Electrical Characteristics and Specifications
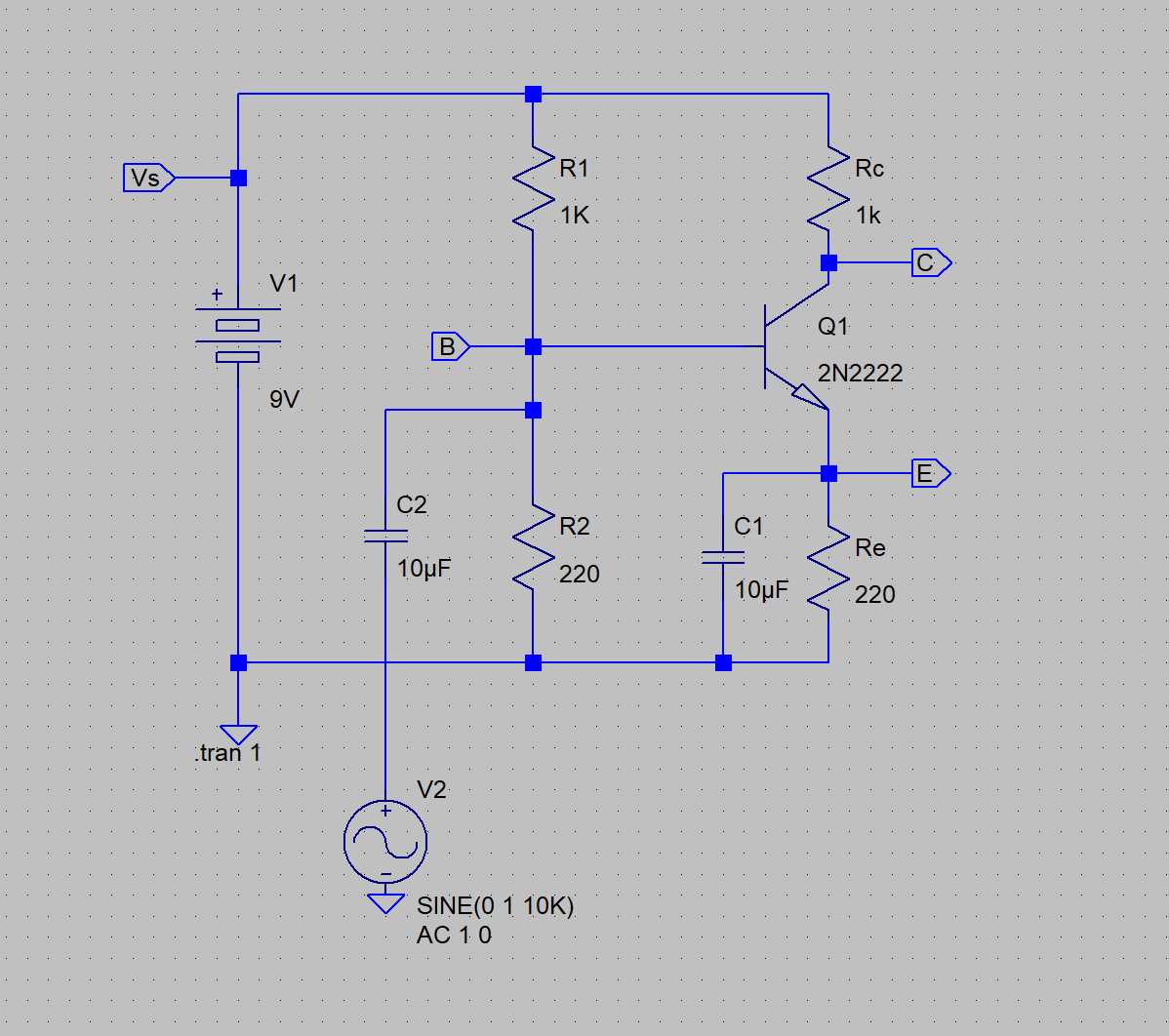
In this section, we will explore the vital electrical characteristics and specifications relevant to the 2n2222a 331 transistor. These parameters provide crucial information about the performance and capabilities of the transistor, allowing engineers and designers to make informed decisions when integrating it into their circuits.
1. Gain
The gain of a transistor refers to the amplification factor of the input signal. It indicates the ratio of the output current to the input current. The 2n2222a 331 transistor offers a high gain, ensuring efficient and reliable signal amplification.
2. Maximum Collector Current
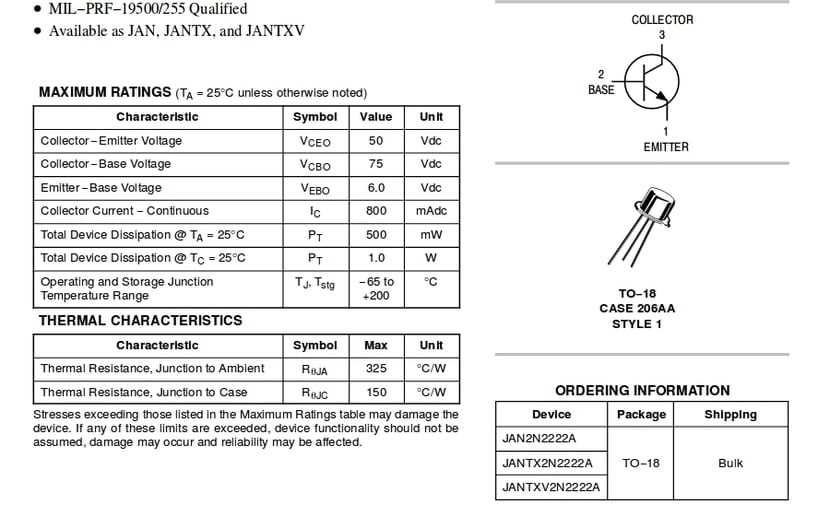
The maximum collector current represents the highest current that the transistor can handle without risking damage. It defines the transistor’s ability to support high-power applications, making it suitable for various electronic projects that require robust current-handling capabilities.
3. Voltage Ratings
The voltage ratings specify the maximum voltage that the transistor can tolerate before breakdown or failure. These ratings are crucial in determining the transistor’s compatibility with specific voltage levels in a circuit.
4. Power Dissipation
The power dissipation refers to the amount of power that the transistor can handle and dissipate without overheating. This parameter is essential in preventing thermal damage to the transistor and ensuring its reliable operation under different load conditions.
5. Frequency Response
The frequency response of the 2n2222a 331 transistor refers to its ability to handle signals at different frequencies. It is crucial in applications where the transistor needs to accurately reproduce input signals within a specific frequency range.
By understanding these key electrical characteristics and specifications of the 2n2222a 331 transistor, engineers can select and utilize this component effectively in their circuit designs, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Application Circuit Design and Considerations

In this section, we will explore the design and considerations involved in the application circuit for the components under discussion. The focus will be on optimizing performance and ensuring reliable operation.
When designing the application circuit, it is important to carefully select the appropriate components to achieve the desired functionality. Additionally, consideration should be given to the specific requirements and constraints of the application, such as power supply, temperature range, and signal characteristics.
Circuit layout plays a crucial role in the overall performance of the application circuit. Proper placement and routing of components, as well as minimizing parasitic effects, will help reduce noise and improve signal integrity. Grounding techniques and decoupling capacitors should also be implemented appropriately to prevent instability and ensure consistent operation.
Furthermore, thermal management should not be overlooked when designing the application circuit. Heat dissipation mechanisms such as heatsinks or thermal pads should be employed, especially if the components are expected to operate at high temperatures or handle significant power levels. Failure to adequately address thermal management can lead to performance degradation or premature failure of the circuit.
Signal conditioning is another crucial consideration in application circuit design. Depending on the application requirements, additional components such as amplifiers, filters, or voltage regulators may be needed to condition the input or output signals. It is important to select the appropriate signal conditioning components to achieve the desired signal quality and ensure compatibility with the rest of the circuit.
In summary, careful consideration should be given to all aspects of application circuit design and the specific requirements of the application. Proper component selection, circuit layout, thermal management, and signal conditioning are all key factors in optimizing performance and ensuring reliable operation.